In the rapidly evolving world of printing technologies, digital and offset printing are predominant methods. Each offers unique benefits and limitations based on a project’s specific needs. This article compares these two printing techniques comprehensively, exploring their processes, applications, cost-efficiency, quality, and environmental impacts. Understanding the distinctions between digital and offset printing can guide businesses, designers, and consumers to make informed decisions for their printing projects.
Overview of Digital Printing
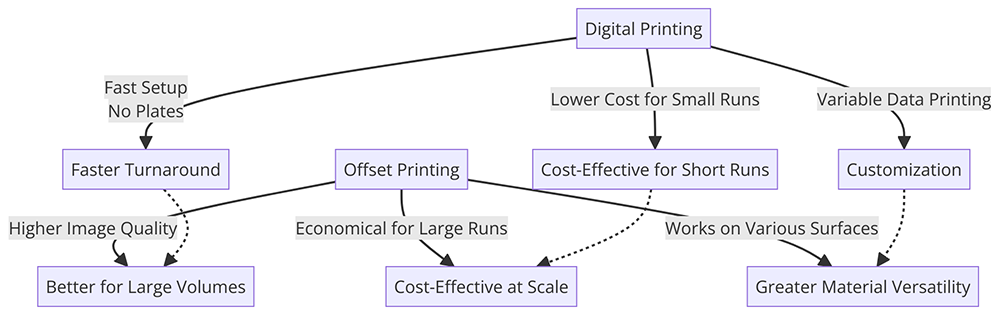
Definition and Process: Digital printing refers to printing methods from a digital-based image directly to various media. It primarily involves using large-format and high-volume laser or inkjet printers. This technique eliminates the need for a printing plate, which is used in traditional methods like offset printing.
Key Features:
- Speed: Digital printing provides quicker turnaround due to less physical setup and immediate print-to-media output.
- Cost: It is cost-effective for short runs because it requires less setup time and materials.
- Customization: Offers high customization options such as variable data printing, where each piece can have unique information.
Overview of Offset Printing
Definition and Process: The dominant industrial printing technique is offset printing, also known as lithography. Images on metal plates are transferred (offset) to rubber blankets or rollers and then to the print media. The process requires the creation of plates, one for each color.
Key Features:
- Quality and Versatility: Produces sharp, clean, high-quality prints with detail and color fidelity.
- Efficiency: More cost-effective than digital for high-volume printing as the unit cost decreases as the quantity increases.
- Material Versatility: Printable on various substrates, including paper, cardboard, plastic, and metal.
Comparison Criteria
Print Quality
- Digital Printing: The quality of digital printing has significantly improved over the years. It offers excellent quality with richer blacks and finer detail reproduction and is close to, if not, rivals offset.
- Offset Printing: Known for its image quality, precision, and color accuracy, offset printing uses actual Pantone inks and is often required for projects that require exact color matching.
Cost Considerations
- Digital Printing: Ideal for lower-volume projects due to minimal setup costs. It becomes comparatively expensive as the print volume increases.
- Offset Printing: Involves higher initial setup costs, making it less ideal for small runs. However, it is more cost-effective for large runs as the price per unit decreases significantly.
Turnaround Time
- Digital Printing: Offers a faster turnaround due to the lack of plate setup. It is highly efficient for meeting tight deadlines.
- Offset Printing: The setup for offset printing is time-consuming due to plate production and ink setting, resulting in longer lead times.
Customization and Versatility
- Digital Printing: Highly versatile for personalized projects. It is perfect for direct marketing as it allows for customizing individual graphics and text in a print run.
- Offset Printing: Offers limited flexibility in customization post-setup. Each change in the print content requires new plates, making it inefficient for variable data projects.
Environmental Impact
- Digital Printing: Generally considered more environmentally friendly due to less chemical and paper waste during setup. It also tends to use less energy.
- Offset Printing: Generates more waste due to the materials (plates, chemicals, paper) and energy required for setup. However, strides are being made to reduce its environmental footprint through recycling and renewable energy sources.
Applications and Suitability
Digital Printing: Ideal for on-demand printing, small to medium-sized jobs, personalized printing, and prototypes. They are commonly used in desktop publishing, variable data printing, print-on-demand, and producing sharp, professional-looking documents.
Offset Printing: Best suited for commercial large-volume printing like newspapers, magazines, brochures, stationery, and books. Preferred for jobs that require high print quality and color fidelity over large print runs.
Conclusion
Choosing between digital and offset printing depends mainly on the specific needs of the print job. Digital printing is preferable for those requiring quick, cost-effective prints in smaller quantities or with varying data. In contrast, offset printing remains the best option for high-volume, high-quality printing tasks that demand color precision and material versatility. By considering factors such as print quality, cost, production time, environmental impact, and the project scope, businesses and individuals can select the most appropriate printing technology for their needs.
This analysis highlights the advantages and limitations of digital and offset printing, providing a clear guide for users to make informed choices based on their particular printing requirements.
Ink Etc Marketing offers both digital and offset printing. Call today to discuss your next project!